INTERDEPENDENCE AMONG LIVING ORGANISMS
1. A specific group of organisms that have the same characteristics is known as species.
2. Organisms from the same species mate together to produce offsprings, for example the species of
Home sapience.
3. Organisms of the same species that live and reproduce in a particular habitat will form a
population. For example, in a pond habitat there are populations of fish, shrimps and water
hyacinths.
4. A habitat is the place where on organism stays in its naturel state.
5. In a habitat, an organism can eat reproduce and get shelter.
6. Habitat of several organisms :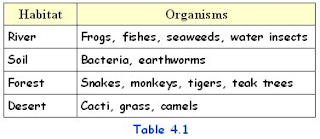.png)
7. A community is formed when a few populations of different types of animals and plants live a
habitat. An example of a community is the population of animals ( fish ) and plants ( weeds ) living
together, interacting and influencing each other in a pond.
8. An ecosystem is formed when a community of living organisms in a habitat interacts with one
another as well as with the non-living environment.
9. An ecosystem consist of the living or biotic components in the environment.
10. The biotic components in an ecosystem are plants, animals and microorganisms.
11. The non-living components of an ecosystem or abiotic components consist of water, gases, light,
soil, temperature and rocks.
12. The eco-balance of the environment is closely related to the oxygen cycle, carbon dioxide cycle,
nitrogen cycle and food web.
13. Human beings are part of the ecosystem because they depend on living things and non-living
things in order to survive. If the ecosystem is interrupted, human lives will also be disturbed
14. A few elements in an ecosystem need to be maintained in order to keep the ecosystem balance :
(a) The size of each population.
(b) The composition of gases in air, water and soil.
(c) The composition of mineral salts in the soil.
15. The biotic and abiotic components are interdependent with one another to create a balanced
ecosystem which changes only slighly over time.
.png)